Release time :2023-03-23
Source:support@yingchitech.com
Scan:1751
Non-invasive neuromodulation technology is a bioengineering technology that uses non-implantable technology to stimulate nerve fibers physically or with drugs to regulate neuronal activity, so as to achieve certain therapeutic effects. Non-invasive regulation has many advantages, such as painless, safe, inexpensive and adjustable parameters and targets, so it has broad prospects for development in the future.
In recent years, neuromodulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation, have developed rapidly and become an effective tool in clinical treatment.
Transcranial direct current stimulation(tDCS) is a non-invasive neural regulation technique that utilizes constant weak direct current (1.0~2.0 mA) to subthreshold regulate neuronal membrane potential and change cortical excitability. Transcranial direct current stimulation(tDCS) consists of two surface electrodes, negative and positive, known as polarity characteristics. Different parameter settings (such as polarity, stimulation site, current intensity, and stimulation method) can produce different biological effects.
transcranial magnetic stimulation(TMS) is a noninvasive neural regulatory program that allows magnetic signals to stimulate brain neurons without attenuation, producing excitatory or inhibitory effects. According to the stimulation mode, TMS is divided into single pulse TMS (sTMS), paired TMS (pTMS), deep TMS (dTMS), repetitive TMS (rTMS), and θ Theta burst stimulation (TBS) mode.
In the tDCS evidence-based evidence published in the journal of neuropsychopharmacology in 2020, depression, schizophrenic auditory hallucinations, addiction and obsessive-compulsive disorder were included in the field of mental diseases. Among them, depression is recommended as Grade A, which is accurate and effective. Schizophrenic hallucinations and addictions are recommended as Grade B, and obsessive-compulsive disorder is recommended as Grade C. For depression, the anode is placed on the left DLPFC, and the cathode is placed on the right DLPFC or orbitofrontal lobe.
there are two clear guidelines for depression to incorporate transcranial direct current stimulation(tDCS) into clinical use. Canada's CANMAT 2016 clinical guidelines believe that tDCS can be used as a third-line treatment for patients with depression who are ineffective in receiving one antidepressant treatment. British NICE clinical guidelines point out that transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) can be used to treat depression or relapse of depression.
In 2008, FDA approved TMS for the treatment of major depression;
In 2013, FDA approved TMS for the treatment of migraine;
In 2020, FDA approved TMS for the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD);
In 2021, FDA approved TMS for the treatment of depression with anxiety symptoms.
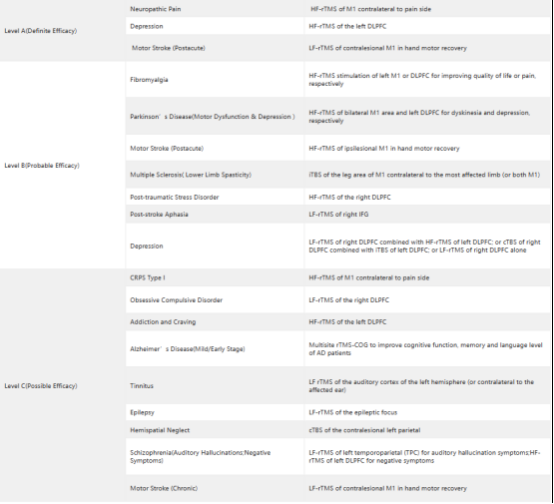
Table 1 Guidelines of TMS Therapy